The embedded processors is the core of the embedded system, and it is the hardware unit that controls and assists the operation of the system. The range is extremely wide, from the original 4-bit processor, the 8-bit single-chip microcomputer that is still widely used at present, to the latest 32-bit and 64-bit embedded CPU that are widely favored. There are more than 1,000 types of processors with embedded functions in the world, and the popular architecture includes more than 30 series such as MCU and MPU.
In view of the broad development prospects of embedded systems, many semiconductor manufacturers have mass-produced embedded processors, and the company's own design of processors has become a major trend in the future embedded field. Various varieties, faster and faster, stronger and stronger performance, and lower and lower prices. The addressing space of the embedded processor can be from 64kB to 16MB, the processing speed can reach 2000 MIPS at the fastest, and the package ranges from 8 pins to 144 pins.
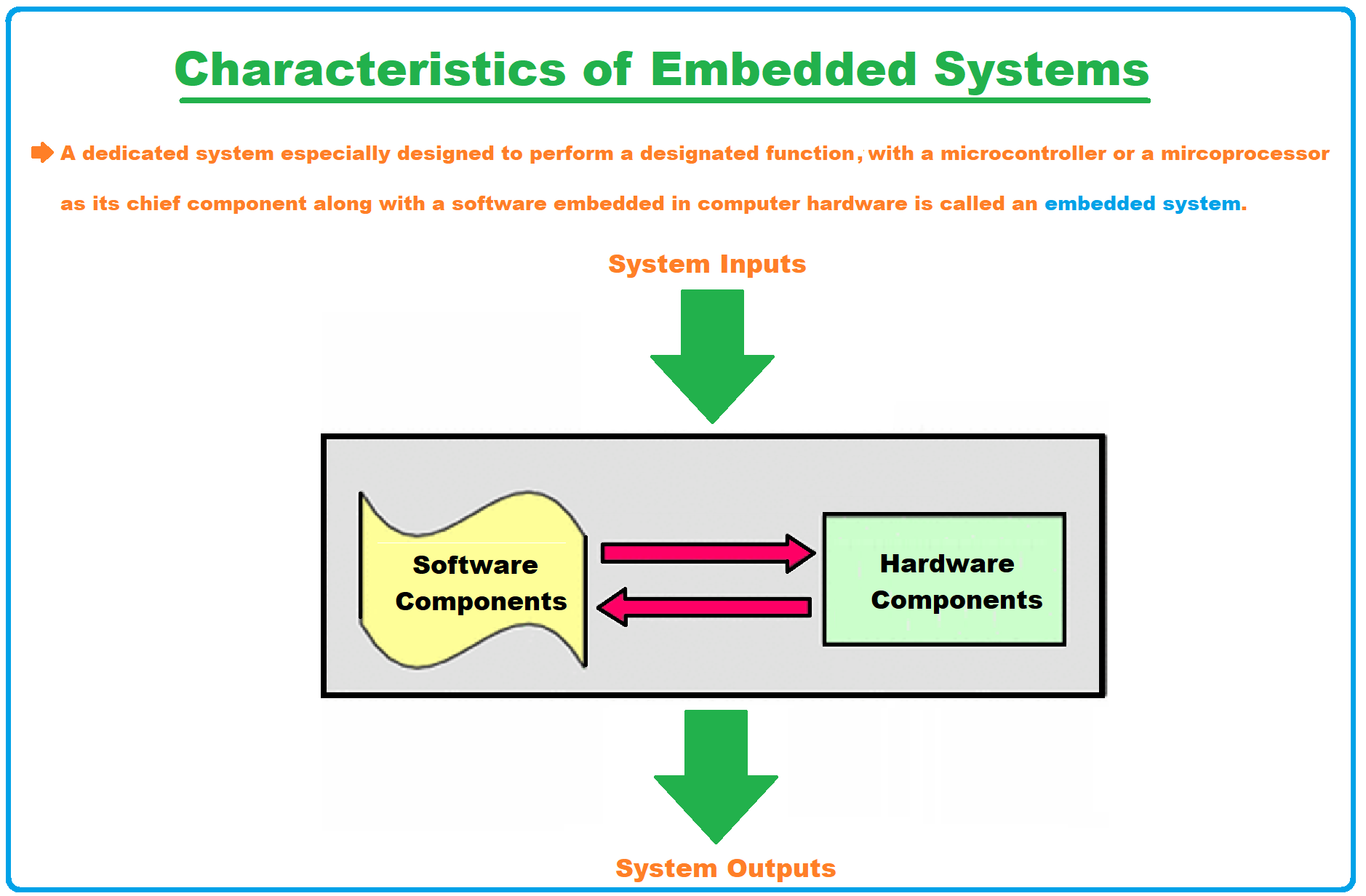
Characteristics of Embedded System
Embedded microprocessors are similar in basic principle to those of ordinary desktop computers, but have higher working stability, lower power consumption, and strong adaptability to the environment (such as temperature, humidity, electromagnetic field, vibration, etc.) , smaller size, and more integrated functions.
In the field of desktop computers, the main index when comparing processors is the calculation speed. From the 386 computer with a main frequency of 33MHz to the PenTIum 4 processor with a main frequency of 3GHz, the improvement of speed is the change that users are most concerned about. field, the situation is completely different. The choice of embedded processor must be based on the design requirements, among many factors such as performance, power consumption, function, size and packaging form, SoC level, cost, commercial considerations, etc., to make a compromise and choose the best.
Types of Embedded Systems
1. Microprocessor
The embedded microprocessor (Micro Processor Unit, MPU) is evolved from the CPU in the general-purpose computer. It is characterized by a processor with more than 32 bits and high performance, and of course its price is correspondingly high. However, unlike computer processors, in actual embedded applications, only the functional hardware closely related to the embedded application is reserved, and other redundant functional parts are removed, so that the embedded application can be implemented with the lowest power consumption and resources. special requirements. The main types of embedded processors are Am186/88, 386EX, SC-400, Power PC, 68000, MIPS, ARM/StrongARM series, etc.
2. Microcontroller
The typical representative of embedded microcontroller (Microcontroller Unit, MCU) is a single-chip microcomputer, which integrates ROM/EPROM, RAM, bus, bus logic, timer/counter, watchdog, I/O, serial port, pulse width modulation Various necessary functions and peripherals such as output, A/D, D/A, Flash RAM, EEPROM, etc.
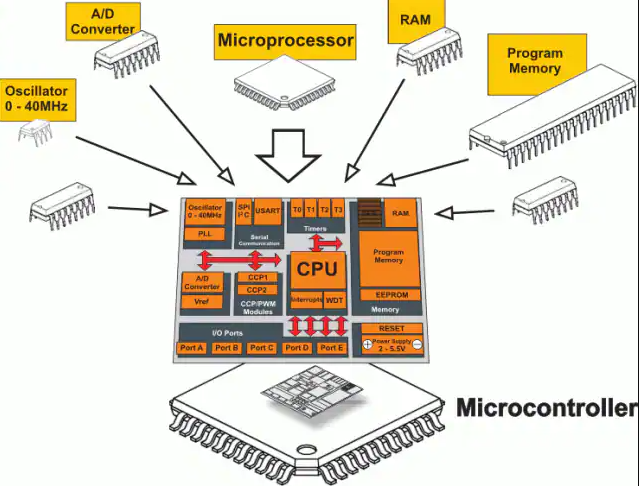
Compared with embedded microprocessors, the biggest feature of microcontrollers is single-chip, which greatly reduces the volume, thereby reducing power consumption and cost, and improving reliability. Microcontrollers are the mainstream of the embedded system industry. The on-chip peripheral resources of the microcontroller are generally abundant and suitable for control, so it is called a microcontroller.
Due to the low price and excellent functions of MCU, it has the largest variety and quantity, and the more representative ones include 8051, MCS-251, MCS-96/196/296, P51XA, C166/167, 68K series and MCU 8XC930/ 931, C540, C541, and support I2C, CAN-Bus, LCD and many dedicated MCU and compatible series. MCU accounts for about 70% of the embedded system market share. The Avr single-chip microcomputer produced by Atmel has a high cost performance because it integrates devices such as FPGA, and it is bound to promote the development of the single-chip microcomputer.
3. DSP processor
The embedded DSP processor (Embedded Digital Signal Processor, EDSP) is a processor specially used for signal processing. It has a special design in terms of system structure and instruction algorithm, and has high compilation efficiency and instruction execution speed. DSP has been widely used in various instruments such as digital filtering, FFT, and spectrum analysis.
The most widely used is TI's TMS320C2000/C5000 series, and Intel's MCS-296 and Siemens' TriCore also have their own application ranges.
4. System on a chip
Embedded System On Chip (System On Chip): SoC is one of the hot topics in the field of embedded applications, which pursues the largest integrated device in the product system. The biggest feature of SOC is that it successfully realizes the seamless combination of software and hardware, and directly embeds the code module of the operating system in the processor chip. Moreover, the SOC is highly comprehensive, using hardware description languages such as VHDL inside a silicon chip to realize a complex system.
Since SOCs are often dedicated, most of them are unknown to users. A typical SOC product is Philips' Smart XA. A few general-purpose series such as Siemens' TriCore, Motorola's M-Core, some ARM series devices, Neuron chips jointly developed by Echelon and Motorola, etc. Related Reading: 18 Basic Principles of Single Chip Selection
It is expected that in the near future, some large chip companies will repel competitors in one fell swoop by launching mature SOC chips that can occupy most of the market. SOC chips will also play an important role in application fields such as sound, image, film and television, network and system logic.
Embedded Processor Summary (Common)
(1) Embedded ARM microprocessor (embedded microprocessor structure)
ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) can be considered not only the name of a company, but also a general term for a type of microprocessor, or the name of a technology. ARM microprocessor is currently a processor with a very wide range of applications. So far, the application of ARM microprocessors and technologies has almost spread across various product markets such as industrial control, consumer electronics, communication systems, network systems, and wireless systems. , into various fields.

(2) Embedded MIPS processor
MIPS is a very popular RISC processor in the world. MIPS means "microprocessor without internal interlocking pipeline stage", and its mechanism is to use software methods to avoid data-related problems in the pipeline as much as possible. MIPS Technology Corporation is a well-known chip design company in the United States. It uses the simplified instruction system computing structure (RISC) to design chips. It designs and manufactures high-performance, high-end and embedded 32-bit and 64-bit processors. In RISC processors occupies an important position.
(3) PowerPC
The PowerPC Architecture Specification (PowerPC Architecture SpecificaTIon) is a chip developed by IBM (International Business Machines Corporation), Apple (Apple Corporation) and Motorola (Motorola) in the 1990s, and a PowerPC-based multiprocessor computer was manufactured. . The PowerPC architecture is characterized by good scalability, convenience and flexibility.
(4) Embedded X86 processor
x86 is an abbreviation for the standard number of an Intel Embedded processor general-purpose computer series, and also identifies a set of general-purpose computer instruction sets. X has nothing to do with the processor. It is a simple wildcard definition for all *86 systems, for example: i386, 586, Pentium. Compared with ARM and MIPS, the application range of embedded processors of X86 architecture is narrower. It is mainly used in desktop and low-end server processors.
(5) Embedded DSP processor
 DSP is a special processor for high-speed real-time processing after the analog signal is converted into a digital signal, and its processing speed is 10 to 50 times faster than the fastest CPU. Under the background of today's digital age, DSP has become the basic device in the fields of communication, computer, consumer electronics and so on. Industry insiders predict that DSP will be the fastest-growing electronic product in integrated circuits in the future, and will become a decisive factor in the upgrading of electronic products.
DSP is a special processor for high-speed real-time processing after the analog signal is converted into a digital signal, and its processing speed is 10 to 50 times faster than the fastest CPU. Under the background of today's digital age, DSP has become the basic device in the fields of communication, computer, consumer electronics and so on. Industry insiders predict that DSP will be the fastest-growing electronic product in integrated circuits in the future, and will become a decisive factor in the upgrading of electronic products.